The bombs dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki and the atmospheric bomb tests carried out in the 1950’s and ‘60’s were the tragic results of deliberate and premeditated actions. Many of the releases of radiation from the military or civilian nuclear industry, however, are well and truly accidental.
Nuclear accidents in the military domain date back to the early days of the arms race, when the major powers – United States, Soviet Union and Great Britain – developed their atomic weapons wit the greatest possible secrecy.
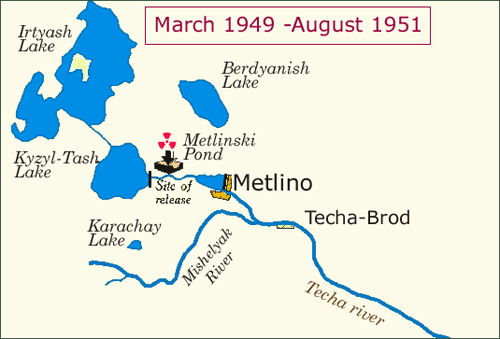
1950, Mayak: a military accident:
In the 1950’s, at the beginning of the Mayak reactor, the waters of the Kyzyltash lake were directly used to cool the core of the plutonium-producing reactors. Later on, low and intermediate level radioactive waste directly discharged to the Techa River were responsible for serious environmental contaminations. A contrast should be noted between military and civilian nuclear accidents: in the first case such as Mayak, serious accidents have been covered up for years by secrecy, whereas there was tremendous media hype around the Three Mile Island accident, which caused more fear than actual damage.
© DR(Source Richard Wilson et al)
These early accidents were the result of a combination of a lack of experience, ignorance of many relevant phenomena, and a general disregard for necessary safety precautions. Environmental consequences did not weigh heavily against strategic objectives. The Soviet Union in particular erlied on wide open spaces to mitigate the harmful effects of the laxity then under way.
Thereby the Técha river in the south of the Urals was contaminated from 1949 to 1956 by radioactive waste discharged directly into lakes and a waste storage tank exploded for lack of cooling on the same site of Mayak.
The 1957 graphite fire at the Windscale power plant (better known as the Sellafield reactor) would have had far less dramatic consequences if the English engineers had known about the Wigner Effect, a then comparatively recently-discovered phenomenon. Many of these accidents which took place on old military sites were understandably late to emerge – especially those which took place in the old Soviet Union.
The losses of nuclear weapons during air transport should be included : 14 in all, the best known of which were those that occurred in 1966 in Palomares (Spain) and in 1968 in Thule in Greenland, with rejection of plutonium-239. Submarine weapons and reactors have also been lost at sea. The radioactive risk is minimal in the case of uranium weapons.
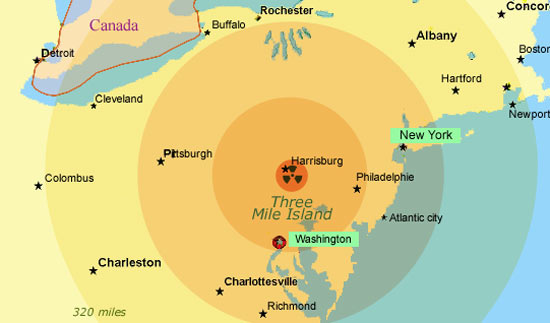
Three Mile Island : a reactor accident in 1979
The mass evacuation following the TMI accident coincided with the release of a nuclear disaster movie starring Jack Lemmon, Jane Fonda and Michael Douglas, ‘The China Syndrome’. In the film, journalists report events in a top secret nuclear reactor while the authorities attempt to suppress the story. The humoristic title comes from a belief, that if an American nuclear reactor melts down it will melt through the Earth coming out on the other side, in China! In the real-life accident, fusion did take place in the reactor’s core, but the surrounding layers remained intact. The circles on the map above show the extent of feared fallouts that never took place.
© IN2P3
The civilian nuclear industry profited from many of the painful lessons teached by the military accidents. A security-oriented culture began to develop, and the nuclear industry took pride in the lack of any major accidents. The 1977 Three Mile Island accident and especially the 1986 Chernobyl disaster, however, shook the public’s confidence in this new technology.
The Three Mile Island accident, which took place near Washington DC, resulted in the destruction of a reactor but fortunately caused comparatively little environmental contamination. The traumatic effect it left on the American psyche was mainly due to the precautionary displacement of several hundreds of thousands of people. The security systems which prevented the Three Mile Island accident from transforming into anything more serious were also in place on the Chernobyl reactor. The dramatic consequences of Chernobyl were largely the result of the tragic deactivation of the security systems, and the giant radioactive cloud which has come to represent the Soviet disaster would otherwise have been avoided.
The last accident of Fukushima was triggered by the tsunami that devastated Japan in March 2011. The reactors at the plant were shut down but were their cooling systems were drowned. After Three Mile Island, the Japanese disaster has confirmed that defects of a proper cooling after shut down, as well as control of the chain reaction, could be the source of the more severe accidents.
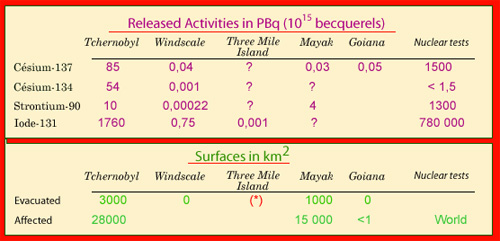
Comparison of major accidents
To effectively compare the major accidents with the fallout caused by nuclear testing, two factors have been considered: the activity of the most important radioisotopes released, and the surface area affected by the radiation (or the surface area evacuated as a result). In the case of Three Mile Island in 1979, for instance, while there was no permanent evacuation, some 100,000 people freely decided to temporarily vacate their own homes.
© IN2P3 (Source UIP/EULEP/EURADOS)
Reactor accidents are not the only ones that can take place, as shown by the 1999 TokaïMura criticality accident. Workers at this Japanese fuel reprocessing facility violated the security regulations that were in place, resulting in a comparatively minor accident nevertheless considered to be the third most serious in the history of nuclear technology.
Last but not least there are the accidents linked to radioactive sources used in medicine, industry, or in laboratories. The risk of exposure mandates a rigorous inspection system, but the small amounts of radioactivity involved limit the potential consequences of such accidents.
Articles on the subject « Nuclear Accidents »
The INES scale
The severity scale of nuclear accidents Nuclear installations and their operation are complex and[...]
Accidents of radioactivity
The importance of a close monitoring of radioactive sources… In many countries, the possess[...]
Accident Causes
Human errors, design flaws and natural cataclysms A nuclear accident dwarfs all other types of ac[...]
Mayak Accident
A military long-hidden nuclear accident of the Soviet era Long before Chernobyl, it was suspected[...]
Windscale Accident
Windscale : an accident of the U.K nuclear weapon program (1957) The fire which occurred the 10th[...]
Three Mile Island
1979: A major accident that led to the destruction of a reactor The Three Mile Island plant (TMI)[...]
Tokaimura Accident
1999 : a “criticity” accident in Japan This surprising accident of “criticality[...]