Provide the best safety for reactors during decades
Nuclear reactors are designed to operate for many years, at least 40 years in France, more in the United States where 38 units had already passed that age in 2014. In addition to the permanent control and monitoring of the reactor operation, a high quality maintenance should be provided to insure a safe functioning during decades.
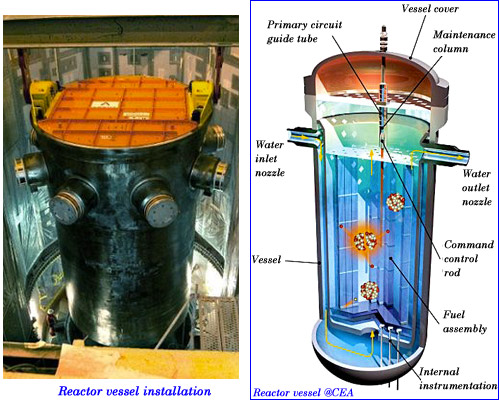
The reactor vessel, an irremovable component …
This steel tank ensures containment of radioactive material produced in a reactor core. This major component that cannot be replaced should ensure that containment throughout the decades of a reactor life. Steel PWR reactor vessels are designed to withstand high temperatures reached in the heart – about 300 ° C – and a pressure of 150 bars. It should also resist against aging and embrittlement due to neutrons.
© CEA
In France it is the Nuclear Safety Authority (ASN) associated with the Institute for Radiological Protection and Nuclear Safety (IRSN) for technical aspects that monitors and tracks the condition of the reactors operated by the utility company EDF. The ASN is responsible for verifying compliance by the latter of its obligations in radioprotection and nuclear safety. In case of non compliance, the agency has the power to stop a reactor and to impose sanctions.
The authorization to operate a nuclear installation is issued for an unspecified time. It is however called into question by ASN every ten years during a safety review, the decennial visit. The purpose of the decennial visit is twofold: to examine in depth the status of the installation, taking into account its aging: improving its security level by taking advantage of feedbacks and technical progress in the reactor technology achieved.
The average duration of about 3 to 4 months of decennial visits gives time to achieve the regulatory controls, to make the necessary replacements and implement the agreed changes to improve the safety of the facility.

Replacement of a steam generator
Steam generators are among the major reactor components, which not subjected to direct irradiation like core vessels, can be replaced during the life of a reactor. One takes advantage of decennial visit long shutdowns to make these replacements, here at the Blayais power plant near Bordeaux. The operation is tricky. To leave the containment building, the voluminous steam generator has to find its way through a real mouse hole
© EDF
During the full check-up performed under supervision of the Nuclear Safety Authority (ASN), three major components of facilities are inspected in particular : the reactor vessel; the primary circuit; the reactor containment building.
Reactor vessel : During the decennial check-up the wall welds of its coating are inspected. The intense neutron flux close to the reactor core can on the long term weaken the steel quality . If the reactor goes beyond 40 years, it should be demonstrated that the incurred risks would remain under control. This risk limitation relies on the intrinsic high quality of the vessel and on the periodic inspections that ensure the absence of default in the areas the most exposed to radiations ….
Primary circuit : The primary circuit undergoes a hydraulic test during the decennial visit. The test consists in putting the circuit at a pressure of 206 bars, 1.2 times its design pressure. Faucets, pipe sections (within and outside the main primary circuit) are replaced. In parallel, one replaces steam generators, command clusters, various sensors or parts of control and command devices.
Containment building : The containment is checked for leaks and its mechanical strength. The decennial inspection consists in isolating the walls of the building housing the reactor and to bring inside a 4 atmospheres pressure during16 hours in order to prevent potential radioactive releases outside.
Towards a “great carenage” in France ….
French reactors reached their fourth decennial inspection and the age of 40 years after 2019. The oldest one, the iconic Fessenheim reactor, was the subject of a campaign promise of French president François Hollande in 2012. It has been shut down before the end of his term, despite EDF, staff and local population wishes.
Will it be necessary to extend the lifetime of the french PWR fleet beyond 40 years, thanks to what EDF call its grand carenage, a major refit. If France were to shut down a large number of reactors from 2019 to reach the target of 50% of nuclear electricity in 2025, the EDF network would have, each year from 2019 to 2025, to put off 5 gigawatt of electric power the power to supply five million homes. The green energies assumed to bridge this, solar and wind energy, depend on the sun and wind and cannot do it 24 hours a day. It is not yet known how to supply such a large amount of electricity.
Germany, which closes its reactors, uses dirty lignite coal plants or gas plants emitting CO2 to compensate in order ensure a constant supply of electricity. This great nation, champion of green energy, was paradoxically in 2016 the most polluting in Europe.
Which option will be the most expensive? Refurbish reactors through their extensive refit would cost, but less than the construction of new reactors. On the other hand, the cost of the solar or wind kilowatt still exceeds the amortized, reactors. In Germany, the cost of electricity for households has doubled. In the USA, where one is pragmatic, many reactors had already gone beyond 40 years of age. Their existence has been extended following their license renewal after a severe examination by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC).
Other articles on the subject « Reactor Safety »
Confining Radioactivity
Three barriers … One major challenges of nuclear installations safety is to master the conf[...]
Reactors Cooling
Evacuate the heat of fissions and radioactive decays To ensure the safety of a reactor requires t[...]
Reactor Shutdown
The embers of fission … When shutting down the reactor, whether for reloading the fuel or a[...]