On-board reactors for submarines and aircraft carriers

1954: Nautilus, the first nuclear submarine
A historic photograph. The Nautilus, the first American nuclear submarine in front of New York skyscrapers in 1954
© US Navy
In addition to conventional land-based power generating reactors, nearly 220 on-board reactors around the world supply the energy needed to propel 150 nuclear vessels and submarines. Nuclear energy is particularly suitable for ships that need to be at sea for long periods without refueling, such as aircraft carriers, cruisers and submarines or icebreakers lost in remote parts of northern Siberia.
The advantage of Nuclear propulsion is to be completely independent of air. Nuclear submatines do not have to surface frequently like conventional submarines. Another advantage : current generations of nuclear submarines never need to be refueled throughout their lifespans, génerally of 25 years .
However, while onboard reactor technology has proven to be ideal and robust for submarine propulsion, it remains prohibitive in size, weight, and costs for the propulsion of merchant ships.
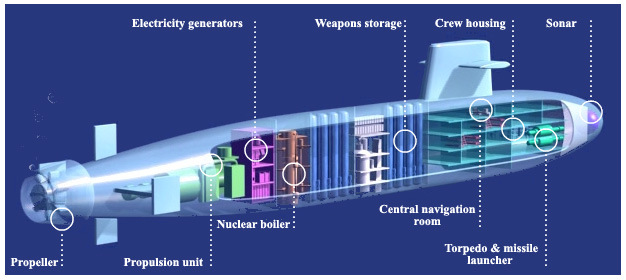
A compact boiler in a cramped room
In a nuclear submarine, the reactor (or to use the dedicated term the boiler room or on-board boiler) is located at the rear of the ship with the propulsion unit. The reactor block, which occupies a limited space, is therefore well separated from the navigation stations and the living quarters of the crew.
© CEA/Défis CEA
Specificities of the naval propulsion nuclear reactors
The purpose of propulsion instead of electricity production, the particularities inherent to warships in the case of submarines and aircraft carriers, and the cramped housing of the nuclear reactor affect the detailed design and technology.
Especially in the case of submarines, auxiliary facilities of on-board reactors such as cooling, ventilation, safety and control systems, are coexisting with the ordinary functionalities of the ship.
While the power of an reactor generating electricity varies slowly, a ship may have to react rapidly during its mission or to escape a threat. The reactor must be able to respond quickly, reliably and safely to the events inherent to the life of submarines or aircraft carriers.
Availability is also essential. For a submarine, the loss of propulsion at sea can be a very serious event that could lead to the loss of the vessel.
The spent fuel is the source of radioactive waste similar to that of power reactors, but in a smaller quantity. The submarine or aircraft carrier reactor core is replaced during a refit. Once its fuel spent, the core of a submarine or aircraft carrier is replaced. Spent fuel is stored in pools or dry storage casks until radioactivity declines. It may be finally reprocessed or ends in an underground repository.

The french aircraft carrier Charles de Gaulle
France has a nuclear aircraft carrier, the Charles de Gaulle, put into service May 18, 2001. The US Navy had in 2009 11 aircraft carriers in service. Large aircraft carriers are equipped with two reactors whose locations are confined in specially secured enclosures.
© Marine Nationale/Emmanuel_Rathelot
Features of on-board reactors
Today, the technology adopted for nuclear propulsion is mainly that of pressurized water reactors (PWRs). The thermal power of these reactors ranges from 10 MWth (thermal megawatts) for prototypes, up to 200 MWth for larger submarines and 300 MWth for aircraft carriers and other surface vessels such as Russian cruisers of the Kirov type. Nuclear powered vessels have generally an electrical power in the range of 35-50 MW (megawatts).
The fuels used are very highly enriched uranium oxides. The enrichment at the beginning of the naval propulsion era was up 80 to 95%, in order to have the maximum instantaneous power (fast dives). It is now rather close to 15%.
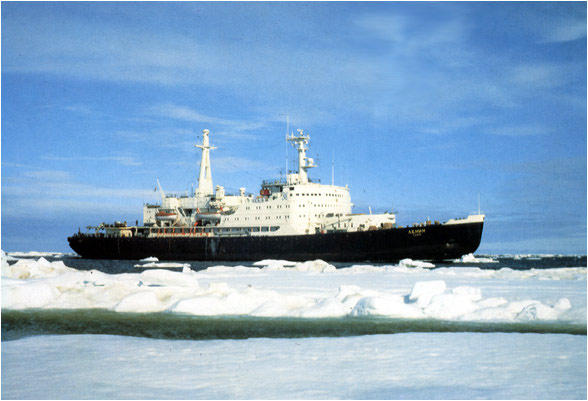

The icebreaker Lenin
The Arctic Ocean north of Siberia is navigable only in summer. Navigation channels are opened by powerful Russian nuclear icebreakers to extend as much as possible the navigation perio . The maneuver to “climb” on the ice to crush it by its weight and then back off and start again – is particularly harsh for the equipment. Russian icebreakers are mainly based in Murmansk, including the six nuclear icebreakers. In 2010, the fleet was aging.
© DR
These reactors should allow variable speed regimes adaptable to the operational circumstances, going from the ordinary cruising speed of submarines to ultra fast speeds in case of diving and intervention : The reactor shoild be able to pass from 10% to 100% of its power in 30 seconds to 1 minute. The cruising speed of large surface vessels is of the order of 25 to 30 knots.
Other articles on the subject « Nuclear Reactors »
Reactor Families
A variety of designs : Natural uranium or enriched uranium as fuel There are several industrial t[...]
World nuclear reactors
A development that takes place today in Asia At the beginning of 2014 the number of reactors in o[...]
Generation I reactors
1950-1970: First generation of reactors (50 – 500 MWe) The first generation reactors were i[...]
RBMK reactors
Soviet-era reactors at Chernobyl Cold War and the Iron Curtain led after 1947 to the development [...]
Generation II Reactors
1970-2009: the rise of nuclear energy About 85% of electricity produced worldwide by nuclear powe[...]
PWR Reactors
The most widespread type of reactor … Pressurised water reactors (PWR) are by far the most [...]
PWR Operation
High pressure water to evacuate heat and slow down neutrons The reactor core is the source of ene[...]
Boiling Water Reactors
BWR or Boiling Water Reactors Boiling water reactors or BWR are in operation in the United States[...]
Candu reactors
Canadian reactors using natural uranium and heavy water CANDU is a nuclear reactor brand develope[...]