Three complementary research areas
The three research areas under the Bataille Act, later supplemented by the 2006 Act, offered a wide range of management methods. The research areas were intended to be complementary rather than competing. Christian Bataille, the promoter of the 1991 Act, did not want any one area to be ‘put on a pedestal’.
For example, although there is no question that large disposal facilities will have to be built, transmutation, which can be used to destroy some of the particularly troublesome waste, could considerably reduce the volume of waste that ultimately needs to be buried. The safety of a geological disposal site will only be enhanced by better conditioning, and sensibly designed storage will make it possible to benefit from technological progress.
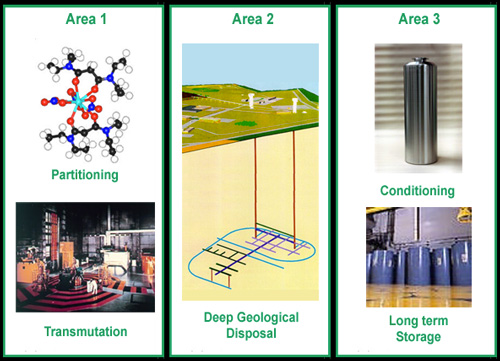
Three research areas
The three research areas defined by the 1991 Bataille Act aim to solve the radioactive waste issues for which solutions have still not been found and to offer an array of management methods. The three areas are complementary. The first aims to explore the potential for separating and destroying certain radioactive atoms. The second aimsto study the deep geological disposasl of high-level waste, which will be inevitable. The third is aiming to improve the conditioning of waste and to enable it to be stored for long periods of time.
© IN2P3
Area 1: Partitioning and transmutation
Research on partitioning looks at the methods for sorting nuclear waste. The intention is to go beyond the partitioning carried out at present, which merely separates the uranium and plutonium from the fission products and minor actinides. For example, the research will look at how to partition a fission product like caesium so that it can be conditioned separately.
Partitioning is particularly useful if it is followed by transmutation. It would then be possible to eliminate radioelements such as the minor actinides, which represent less than one thousandth of the mass of spent fuel but are very long-lived. Transmuting actinides into radioactive products with a short half-life, or even into stable elements, takes nuclear reactions and a return to the reactor. But what kinds of reactors are needed to achieve transmutation that is efficient enough?
Area 2: Deep geological disposal
Can final waste, for which we currently have no other use, be buried deep underground without posing any risks? In what kind of soils can this type of disposal be considered? How can we be sure a disposal facility of this kind will continue to function for long periods of time? For how long should a disposal facility be reversible? If by chance our descendants discovered a way of using the waste, or making it disappear, could we be sure they were able to remove it from the disposal facility?
Area 3: Conditioning and storage
Do good conditioning solutions already exist for multiple types of waste? Can they be improved, made stronger, adapted to the types of radioactive atoms that need to be immobilized?
Do good conditioning solutions already exist for multiple types of waste? Can they be improved, made stronger, adapted to the types of radioactive atoms that need to be immobilized?
Spent fuel and vitrified waste are already stored at facilities designed to last for decades. Could the life of these facilities be extended for periods of up to 300 years? Should these storage facilities be surface or subsurface facilities? How can we ensure that storage facilities that precede but are not designed to replace disposal facilities are monitored and looked after for such long periods of time?
Other articles on the subject « Waste Outlooks »
Area 1: Partitioning
Sorting the radioelements in radioactive waste The separation, or partitioning, of the radioactiv[...]
Partitioning: results
Development of processes and extractant molecules The 2006 assessment of research into partitioni[...]
Advanced partitioning
Partitioning of nuclear waste: hot chemistry Advanced partitioning goes beyond just the partition[...]
Area 1: Transmutation
Area 1: Transmuting or transforming radioactive atoms Transmutation is the second part of researc[...]
Transmutation facilities
Fast reactors and Accelerator Driven Systems (ADS) The neutron, which easily penetrates nuclei, i[...]
Transmutation prospects
A far away objective for Generation IV and 2040… At the time of the first tests on the tran[...]
Area 2: Disposal
Research into deep geological disposal Can the nuclear industry’s final waste, which we cur[...]
Area 3: Long Surface Storage
Research into long-term storage Research into long-term storage is the second research topic in a[...]
Long surface storage concepts
Long-term surface and subsurface storage Research into very long-term storage is a matter for the[...]
Area 3: Conditioning
Area 3: Research into conditioning The conditioning of high-level and intermediate-level waste is[...]