Avoid all contact, ingestion and inhalation
One of the tasks of radiation protection is the decontamination of environments polluted by radioactive substances after an accident.
There is contamination every time radioactive substances are present in the environment or on the surface of an object. Contamination can be the source of exposure,external ,by contact or internal.
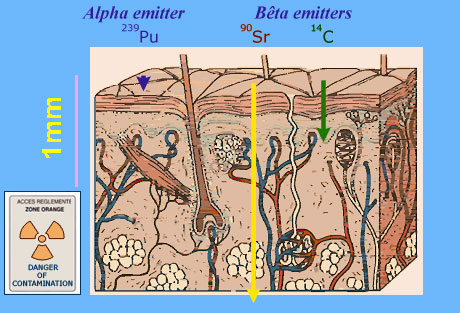
Skin exposition
The skin can be bombarded by alpha or beta rays, either because of the radioactivity in the atmosphere (tritium, carbon-14), or if one touches a surface contaminated by radioactivity. Only Beta rays of sufficient energy, like strontium-90 will reach the deepest part of the skin (the subcutis). Less powerful beta rays like carbon-14 will just reach the dermis. Beta rays of tritium (energetically weak) and alpha because they are quickly stopped (fifty microns) do not pass through the epidermis. The contact with a radioactive source, especially alpha, can lead to burns. The wearing of a protection suit and gloves stops all or mostt of these rays.
© IN2P3
The contact with a radioactive substance or a close proximity are dangerous. Beta and above all alpha rays, being only lightly penetrative, the effects will be intense near the skin but will not be felt deep down. An exposure of this type will therefore cause superficial burns. This is what Henri Becquerel discovered involuntarily. Gamma rays being penetrative, the irradiation is spread throughout the organism, but less intense. The maximum effect is close to the point of contact.
rays being penetrative, the irradiation is spread throughout the organism, but less intense. The maximum effect is close to the point of contact.
It is possible to decontaminate, through a dedicated cleaning, an area, materials and a person who would have been contaminated by contact. The results of the cleaning, dust and other contaminated products taken away will be placed in sealed containers and treated as radioactive waste of low or very low activity.
In the event of a serious accident, one should decontaminate large areas polluted by ground deposition of radioactive particles. At Chernobyl, thousands of liquidators, often poorly protected, cleaned the area around the damaged reactor. At Fukushima, the presence of large amounts of radioactive water had forbidden during long weeks the access to buildings flooded before a decontamination facility to treat these waters was installed.

Decontamination of a school playground after Fukushima
After the Fukushima accident, many schoolchildren parents demanded to the Japanese government that playgrounds were cleaned so that their children may not be exposed to doses exceeding the legal limit of 1 mSv / year. Engines have scraped tis playground to collect the potential deposit of caesium on its surface. The limit of 1 mSv is conservative. The Japanese, whose life expectancy is highest in the world, receive five times more on average because of medical diagnoses.
© Ko Sasaki /The New York Times
Internal contamination happens in three ways: through inhalation of substances or radioactive dust; through ingestion, whilst they remain in the absorbed food or deposited on an object brought to the mouth; through injury with a contaminated object or through the infection of an existing wound. It is impossible to decontaminate a person with an internal contamination as it would be too late. We can however limit the effects of it, for example in the case of tritium, by drinking lots of water.
The nuclear workers protect themselves by wearing specific clothes, gloves and masks (that will become radioactive waste). They check that there are no leaks for these items where radioactive substances are found, as well as the renewal of the air of rooms which is filtered to trap the radioactive dust. The manipulation of very radioactive objects should be done done with robots.
Contrary to a popular view, persons contaminated cannot contaminate other persons and therefore they are not a danger to the people treating them.
Learn more
Other articles on the subject « Radioprotection »
Radioprotection principles
Applying common sense rules according to radiation nature The need for protection from radiation [...]
Gamma Radioprotection
A penetrative radiation more difficult to absorb In the case of ingestion of radioactive substanc[...]
Gamma Attenuation
Attenuation of a gamma beam Of the three types of radiations, gamma rays are the most penetrative[...]
Gamma Absorption
Heavy materials for the absorption of gamma rays In terms of radioprotection mitigate gamma rays [...]
Radioprotection neutrons
A rare radiation, dangerous, penetrating, difficult to absorb The neutron radiation is more penet[...]
Justification and optimisation
In medicine, use of radiation must be justified The ‘Justification and Optimization” [...]
Reglementations and controls
Strict regulations for an efficient radioprotection Radioprotection has a long history. Its princ[...]
Dose legal limits
Applying the precautionary principle and setting cautious limits French regulations set at 1 mSv [...]
Actors in radioprotection
The actors and the basics of radioprotection regulations The rules of radiation protection are no[...]