Acute and chronic exposures
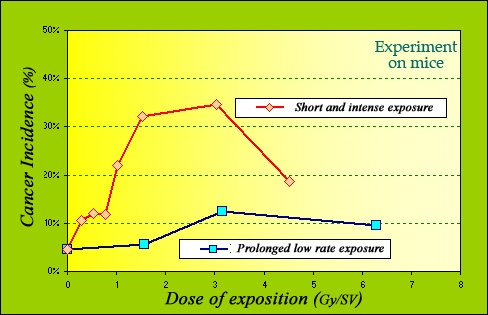
Influence of the dose rates on mices cancers
Decreasing the dose rate, by spreading an intensive dose on a rather long time reduces the risk. Quantitative data are available only for animals, like this comparison of the incidences of cancers on mices between an intense, brief exposures to X or gamma rays and prolonged daily exposures (the total dose is the same). Experience suggests a reduction factor for low rate situated between two and ten. The value of two was used to set acceptable limits for humans.
© IN2P3 (Source IRSN)
The “effective dose” is not sufficient by itself to characterize one exposure to radioactivity. Among the factors to consider, one of the most important is the dose rate that takes into account the duration of exposure.
The exposure to radiation is like the exposure to summer sunrays. Burns of a sunburn result from a short and intense exposure to ultraviolet while skin supports without damaging the same dose received over several hours.
In the case of high doses, there is good reasons to believe that spreading the exposure over time reduces risk. It is likely that cellular repair mechanisms operate at low radiation rates, but are overwhelmed with high rates. This explains the reduced toxicity of low dose rates. However, there are only littlestatistical data in humans on this reduction.
Experiments on animals suggest a reduction factor of between 2 and 10. A better understanding of what happens with humans, would require studies – called epidemiological – on people so-exposed. But cases when high doses rates can be compared to low rates are rare and radioprotection experts stumble again on the impediment of a lack of data in the field.
The influence of dose rate is currently neglected by regulation and legislative texts. For example, the current legislation of radiation protection is based on a linear relationship between the number of cancers and doses. This relationship, itself based on the results of studies on survivors of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, put on the same curve a single and intense exposure whose duration was only a few seconds, as in Hiroshima and Nagasaki or a medical CT-Scan, and chronic exposures, sometimes sparingly issued days after days? This is one of the unsolved problems at the moment.
The International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP website) has begun to consider dose rates in its recommendations. A mitigating factor (called DDREF) is now taken into account in the case of gamma rays to reduce the effects of exposure to chronic low dose rate.
Other articles on the subject « Radiation Effects »
Biological Effects
Living matter: both fragile and robust The amount of damage radiation can cause to living matter [...]
Probabilistic effects
The domain of low and average doses For weak or medium-strength doses, the effects are not as cle[...]
Deterministic effects
The domain of strong doses and severe, reproducible effects For high doses above a certain thresh[...]
Dose-effects Relationship
Can effects caused by low doses of radiations be predicted ? Even though we are constantly expose[...]
Hiroshima Nagasaki Survivors
An exces of cancers and leukaemia among survivors Our knowledge of the risks of cancers due to ra[...]
Low doses effects
Do low doses of radiation have any effect? Radioprotection experts commonly refer to doses below [...]
Linear No-threshold Model
A Precautionary Principle applied to radioactivity … Is it possible to predict the effects [...]
Radioactive Toxicity
A useful indicator but to be used appropriately … The danger presented by a radioactive sub[...]
Dose Factors
What doses when swallowing or inhaling radioactive atoms ? How to evaluate the doses resulting fr[...]