Dating by releasing the energy stored by the radioactivity
Many minerals emit light when heated. This is the phenomenon of thermoluminescence, observed in 1663 for the first time in England by Sir Boyle, who, heating a diamond in darkness, saw that it was emitting a glow.
Later, Pierre and Marie Curie noted the production of intense coloration in glasses and porcelain exposed to radiation and the disappearance of these colors together with the emission of a fluorescent glow when these substances were heated.
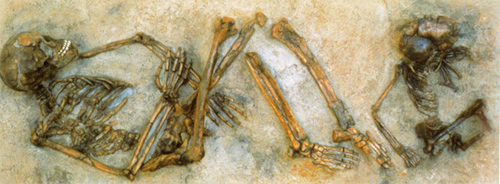
Homo Sapiens
Thermoluminescence dating is a technique that has several applications in Prehistory. The dating is made from minerals found on the site that were heated at the time, such as flints or ceramics (for more recent remains). Thermoluminescence has been used here to date as 92,000 years old this skeleton of a “Homo Sapiens” woman and her child, found in the Qafzeh cave in Israel. This dating has proved that Homo Sapiens could descend from Neanderthals.
© CNRS
Radioactive elements present in clays and soils emit a low and constant flux of rays due to radiatioactive decays of uranium, thorium and their progeny, and potassium-40. These rays lose their energy while passing through the mineral. All electrons released by ionization do not recombine. Some are trapped with an excess of energy in defects and impurities in the crystal lattice. The number of trapped electrons and the energy stored is proportional to time. Heating releases suddenly this energy stored under the effect of radioactivity.
In the case of the glasses of Pierre and Marie Curie, the exposition was short but intense at the point of colouring them. Minerals belonging to ancient archaeological remains have been exposed to the much more modest dose rates of natural radioactivity, but during times much longer. The measure of the stored energy accumulated, which is difficult and requires calibration, allows to evaluate the age of the object being examined.
Thermoluminescence is used in Prehistory. One application is the dating of heated flints, which are abundant in prehistoric sites. It was thus possible to prove that early modern humans (the “proto Cro-Magnon “) had lived on a site in the Middle East nearly 90,000 years ago. They could not be a descendant of Neanderthal men whose a skeleton was found in a layer dated from 60,000 years.
Thermoluminescence dating is also used to date potteries and ceramics in sites that range from the Neolithic period (at the time of polished stones, before the first Egyptian) and the Middle Age. The elapsed time is the one between the moment when the pottery was cooked and when it is heated again for the dating.
Other articles on the subject « Radioactive Dating »
Radiocarbon Dating
Find the age of a bygone object by counting Carbon-14 decays The most common of the radioactive d[...]
Dating in geology
Going back to the distant past In order to date old geological material, geologists rely on radio[...]
Wine Authentication
How to use radioactivity to authenticate a vintage Large quantities of artificial radionuclides f[...]