Principle and implementation of bone scintigraphies
Bone scintigraphy is based on the fixation in the bony structures of phosphate molecules tagged with technetium-99m. The radiopharmaceutical is injected intravenously and no special preparation is needed before the patient examination. The technetium-99m tracer travels through the blood and its uptake by the skeleton is maximal after three hours, which imposes an equivalent waiting period between injection and passage under the gamma camera.
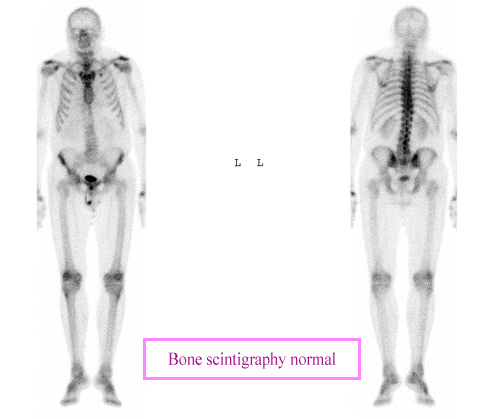
“Whole body” bone scintigraphy
This bone scan shows the fixation of radioactive technetium isotope on the entire skeleton with views from the front (left) and back (right). Bone scans require at least two and a half hours to allow time for fixing theradiopharmaceutical injected to the bone. Scans of the entire skeleton, as for the search for bone metastases, require a “whole body” scan.
© CHU Avicenne
Several types of diagnostics are available :
– Scintigraphic planar images focused on a specific region (the gamma camera is immobilized for several minutes over the region to examine, the knee for example);
– Whole body scintigraphic images, to visualize the tracer fixation throughout the skeleton (the search for bone metastases, for example);
– A tomography exam completing planar images and increasing diagnosis accuracy;
– A complete examination in three phases: study of the vascularization (scintigraphic images performed just after injection) followed by a tissue study and finally a bone scan.
According to the type of review conducted, the tracer fixation is proportional to the vascularization or bone metabolic activity.
Indications for bone scintigraphy:
– Search for bone metastases
– Assesment of primary bone tumor
– Early diagnosis of osteomyelitis
– Stress fracture
– metabolic disease
– painful extremities
– Evaluation of joint prothesis
– articular pathologies (study of the causes and effects of disease or injury).
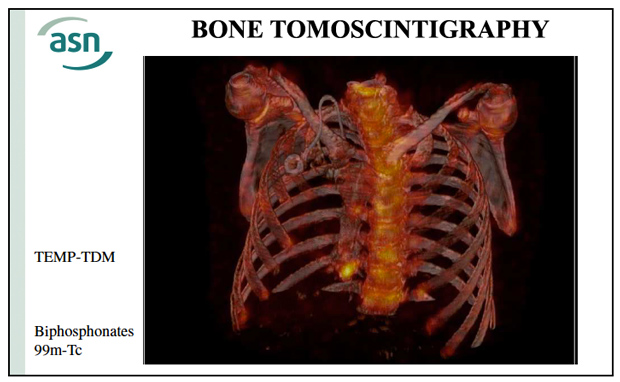
Bone tomoscintigrapy and scanner association
The emergence of tomoscintigraphy (scintigraphy in space) coupled with a CT scan brings a major advance in the scintigraphic exploration of bone lesions. Similar to the combination of PET and CT, the combination of tomoscintigraphy (TEMP) combines functional information from scintigraphy with the morphological data given by scanners (CT or computed tomography).
© ASN
Basic scintigraphies now are more and more replaced by tomoscintigraphy. A tomoscintigraphy consists of the three-dimensional scintigraphy of a the bodypart under investigation. This reconstruction, is obtained with computers by the combination of plane scintigraphic cross-sections taken from different angles.
Radiopharmaceuticals: The Radiopharmaceuticals used are complex molecules tagged with technetium: 99mTc – HEDP, 99mTc – MDP and 99mTc – HMDP.
Other articles on the subject « Scintigraphic examinations »
Nuclear Scintigraphies
A range of diagnoses for determining how the body works … The word ‘scintigraphy̵[...]
Scintigraphic Diagnostics
A tool for non-aggressive analyses of biological functions Diseases are biological processes and [...]
Cardiac scintigraphies
Investigations of the cardiac muscle functionning MYOCARDIAL SCINTIGRAPHY BY PERFUSION Principle [...]